Essential Website Development Requirements: 2025 Guide
The theme of this article is very clear: all the content points directly to one core topic—what essential functions need to be planned when building an independent website. If you’re looking to understand the cost of building such a site, you can refer to a previously published article titled “What Preparations Are Needed for Building an Independent Site and How Much Does It Cost.” As a website with cross-border e-commerce attributes, an independent site needs to have its functional requirements confirmed during the planning stage. Based on past B2C/B2B independent site projects and the features found in well-performing sites across various categories, Logic Digital Technology has compiled this article on “Seven Essential Functional Requirements for Building an Independent Website.” These seven functions comprehensively integrate both B2C and B2B business models. Readers can select the features relevant to their specific business model. These functions cover many aspects of site operation including product display, product sales and payment collection, marketing conversion, website security, and SEO optimization. Each of these features is an indispensable and practical component of an independent website. Together, they form a well-functioning site, with each function playing a crucial or supportive role. In fact, aside from visual creative design, the quality of user interaction and user experience provided by these features largely determines the site's conversion rate and sales performance. Designing, developing, and operating a successful independent website is a systematic project. Overall, this system can be divided into four key parts: visual creative design, user interaction and user experience, marketing conversion functions, and internet marketing capability. These have already been explained in detail in the previously published article “Independent Website Development Planning and Operations.” Because the functionalities required for an independent site are so critical to its success, this article was created to further supplement the theme of “Essential Functional Requirements for Building an Independent Website.”
The article “Essential Functional Requirements for Building an Independent Website” uses simple and easy-to-understand language to explain in as much detail as possible the must-have features of an independent site. The goal is to help businesses that are newly transitioning into independent site projects, as well as readers building an independent site for the first time, to have a clear and organized thought process when planning the functionalities of their site. By understanding what features are necessary and which ones are not, readers can better define their needs during discussions with a Professional Independent Site Development Company. This also helps avoid potential issues after the site goes live, such as missing functionalities that could negatively affect the site's conversion goals and delay the effectiveness of site operations. The seven major functions discussed in this article align with the sections listed in the table of contents below. Readers can follow the sequence to read through the entire article or click on specific sections to directly jump to the content that interests them.
- Independent Website Conversion Features
- Independent Website SEO Optimization Features
- Independent Website Product Display Features
- Independent Website Payment Features
- Independent Website Security and Privacy Features
- Independent Website Analytics and Tracking Features
- Independent Website Social Media Integration Features
Ⅰ、Independent Website Conversion Features

The conversion functionality of an independent website is of paramount importance. Without excellent user interaction and user experience, the conversion features of an independent website will fail, leading to the loss of potential customers and damaging the website's operation. The reason why the marketing conversion functionality of an independent site is emphasized is that regardless of whether the independent site company chooses custom development or template-based development, the functional requirements are proposed by the independent site company itself. In general, the independent site development company will not proactively recommend functionalities, because the development cost of the independent site is determined by factors such as the number of pages, features, and VI/UI/UX design. Since trust between both parties has not yet been established, the independent site development company may avoid making proactive recommendations to prevent any misunderstandings.
1. Inquiry form (contact form)
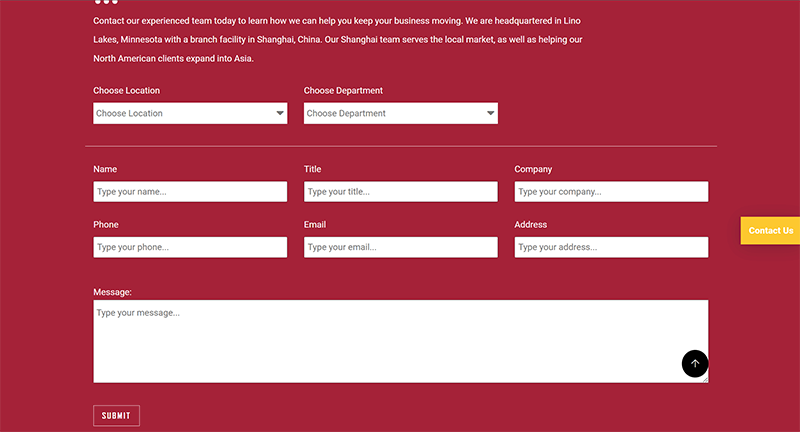
The independent site design typically places the contact inquiry form in the footer of the page and on the Contact page. You can also assign a class ID to the contact form and set the URL of the contact form to the class ID on a button. This way, the form can be integrated into the button, and when users click the button, the contact form window will pop up. Providing multiple entry points for the contact inquiry form makes it easier for users to interact with the site, which in turn can increase the likelihood of users making inquiries. It is important to note that when designing and developing the inquiry contact form, unnecessary fields should be minimized to reduce the difficulty for users filling out the form. The easier the form is to operate, the better the user experience. Additionally, it is recommended to add a spam protection verification method at the bottom of each inquiry form to prevent spam bots from submitting the form. Without a submission verification mechanism, it could cause SMTP mail server crashes and fill up the mailbox with spam. Some readers who are unfamiliar with SMTP forwarding principles might wonder: doesn't the contact form on the independent site send emails through the user's email address? The answer—of course, not. For those without professional computer science knowledge, this confusion is quite normal. If you don't approach the contact form submission from a technical perspective, it’s easy to assume that the form submission is sent from the email address entered by the user. The common elements of an inquiry form (contact form) are as follows:
- Name* (Required): The "Name" field refers to the user's name, and this is a required field that cannot be skipped. It is not recommended to set a fixed format for the Name field, restricting users to fill it in according to specific rules. Instead, users should be allowed to enter their name freely, as we cannot control how users prefer to write their names. Furthermore, whether the user provides their full name or just an abbreviation does not hold significant meaning for us, as we cannot verify the full name and it won't cause us any harm. Therefore, it is not advisable to set unnecessary barriers that would cause inconvenience for the user and lead to them abandoning the form, resulting in a loss of conversions for the independent site.
- Email* (Required): The "Email" field refers to the user's email address, which is also a required field in the contact form, just like the Name field mentioned above. If the email address field is not set as required, the site's operators will not be able to obtain the user's email contact information, and business negotiations cannot continue. Why is this the case? It's simple: without the customer's email address, how can you continue to contact them for business discussions?
- Country: The "Country" field asks users to provide their country/region information. Although collecting users' country/region information is helpful for marketing data analysis, it is not recommended to make this field required, as foreigners tend to value their privacy highly. This is evident from the strict privacy laws in Europe, such as the GDPR. Non-essential information can be left to the user’s discretion to provide.
- Phone: The "Phone" field, like the Country field, is not recommended to be set as a required field. In a world where privacy protection is a global concern, we should not make decisions based on our own usual practices. Thinking from the user's perspective may be more in line with the values of independent site users. The decision of whether to fill in the phone number should be left to the user. For user interaction and experience, the phone input field can be configured with an area code icon or a combination of an area code selection box and number input. Alternatively, users can simply enter the full phone number, but if they choose this method, they may accidentally omit the country/region prefix, causing confusion when the site operator tries to identify the country/region of the phone number. This may result in a situation where the site operator is unable to contact the customer by phone.
- Company: The "Company" field refers to the name of the user’s company. This field is generally set as optional, allowing the user to decide whether to provide the company's information to the independent site. Knowing the user's company details can help the site's operators or sales representatives better understand the customer, deduce the scale of the customer's business, and estimate the potential order volume. However, it is still not recommended to make this field mandatory, as collecting information from customers without a valid reason can lead them to feel uncomfortable, resulting in them abandoning the form.
- Position: "Position" refers to the user's job title. The purpose of including the "Position" field in the contact form is to collect information about the user’s role within their company. For privacy-conscious users, this might feel intrusive. Therefore, the inclusion of the "Position" field should be based on the actual needs of the independent site. If the position is necessary, it can be retained; otherwise, it may be removed from the form.
- Address: The "Address" field refers to the user's address. If necessary, this can be kept, as the sensitivity of privacy around addresses is relatively low. Foreign users typically use addresses for shipping or billing purposes, so it is not likely to raise privacy concerns. However, whether this information is essential for the independent site's operations should be considered, and unnecessary fields should be removed. Ideally, a contact form should focus on simplification, not complexity. For international trade sites, even if we know the customer's address, it is unlikely that we can visit them in person. If we need to send samples, it may be better to use a placeholder in the Address field to explain this or avoid including the address field on the form initially. Instead, we can request the shipping address when communicating with the customer via email.
- Message* (Required): The "Message" field is the main content input box in the contact form. It is the area where users input their inquiry or message, and it serves as the primary purpose of submitting the contact form. This field is required, and if it is not set as mandatory, users might submit the form without providing the necessary information. When the site's operators receive the form without the essential content, they will be confused about the specific inquiry, making it difficult to proceed with the business discussion effectively.
- Verification Mechanism (Required): The "Verification Mechanism" refers to the manual verification step that users need to complete before submitting the contact form. Due to the widespread use of bots to fill out contact forms, a verification mechanism is essential to prevent this behavior. Without a verification system, spammers could overwhelm the site's SMTP resources, filling the inbox with junk emails, which would drain the site's operational efforts. There are two common types of verification systems: one uses a mathematical algorithm that users must solve to prove the submission is legitimate, and the other uses Google's reCAPTCHA program to prevent bots. Both methods can effectively solve the issue of bot-driven spam submissions.
2. Online contact (online customer service)

The display of online contact functions on independent site pages can take various forms, such as the contact toolbar on the right side of the current page you are viewing and the fixed contact information bar at the bottom of the page. These two forms can be used in combination, but it is recommended to use no more than two. Otherwise, too many online contact display formats will affect the aesthetic of the independent site page. It is important to note that when designing page elements for an independent site, the display location of contact information should differ based on the device type. On desktop devices, a user-friendly and visually pleasing approach is to consolidate online contact methods into a contact toolbar and place it on the right sidebar of the page. On mobile devices, however, the online contact (online customer service) button can be fixed directly at the bottom of the page without the need for consolidation. In addition to the layout planning of the online contact tools, it is also necessary to consider which communication tool the independent site should use to achieve effective online communication with customers and best align with the site's conversion goals. Generally, it is not advisable to offer too many communication tools. A row filled with too many options can appear abrupt and cluttered on the page—too much is as bad as too little, and it offers no real benefit. It is recommended to offer only 2–3 tools. For example, on the Logic Digital Technology website, after clicking the customer service button in the right sidebar contact toolbar, only two online communication tools—WeChat and WhatsApp—are provided for users to choose from. As for which communication tool to integrate into an independent site, this should be based on the communication habits of users in the country/region where the site operates. Choosing the most user-friendly tool for the site’s users can encourage them to initiate inquiries. The commonly used and selectable online contact (online customer service) tools are listed below:
- LINE:LINE is an instant messaging tool developed by LINE Corporation, a Japanese subsidiary of the South Korean company Naver. Since its launch in 2011, LINE has achieved great success in Asian markets, especially in Japan and Southeast Asia, thanks to its rich features and convenient user experience. LINE offers powerful core communication functions, allowing users to chat via text, send voice messages, images, videos, and files. It also supports high-definition voice and video calls, enabling efficient communication in both one-on-one and group chats.
- WhatsApp:WhatsApp is a globally recognized instant messaging tool founded in 2009 by Brian Acton and Jan Koum, and acquired by Facebook (now Meta) in 2014. With its clean interface design and strong encryption system, WhatsApp quickly became a key communication platform for users around the world. It offers messaging, voice calling, and video calling over the internet, allowing users to communicate seamlessly across devices and platforms. Users can send text messages, voice notes, images, videos, and files, and also use group chat and broadcast list features for multi-user communication and synchronized information. Unlike many other social apps, WhatsApp has no ads and does not rely on complex social media features, focusing instead on a simple, efficient communication experience—one of the keys to its success.
- Messenger:Messenger is an instant messaging tool launched by Meta (formerly Facebook) in 2011. Initially a built-in chat feature within the Facebook platform, it later became a standalone application and gradually developed into a feature-rich communication platform. Messenger is closely integrated with Facebook accounts—users can log in via Facebook to chat via text, voice, and video calls. It also supports sending images, videos, voice messages, and files, as well as creating group chats for easy team discussions and collaboration. A key feature of Messenger is its cross-platform support—users can access it via mobile devices, the web, or desktop applications without being limited to one device, significantly improving convenience. Additionally, it integrates messaging with Instagram, further breaking down the barriers between social apps and offering a more unified social experience for users.
- LiveChat:LiveChat is an instant messaging tool designed specifically for businesses, mainly used for customer service and sales support on websites and applications. Developed by the Polish company LiveChat Software and launched in 2002, it has become a key solution for businesses worldwide to optimize their customer service process through its efficient real-time chat functions and robust customer management tools. The core feature of LiveChat is its embedded chat window, which allows website visitors to communicate with customer service representatives in real time to resolve issues or handle requests.
3. Call to Action (CTA)

A call-to-action button, or CTA button, is a common element placed in appropriate positions on a webpage to prompt or encourage users of an independent website to take action. CTA buttons can also be referred to as conversion goal buttons and are a key component when planning the conversion path of an independent website. A well-designed CTA button that stands out, is easy to interact with, and does not compromise the visual aesthetics of the page can often help boost conversion rates. The design and development of CTA buttons are generally not technically difficult. However, if the person planning the website is designing an independent site for the first time or lacks a strong understanding of digital marketing strategy, CTA button design is often easily overlooked. As long as they do not affect the overall aesthetics of the page, CTA buttons can be placed on various pages that influence conversion on the website. The judgment of whether the design is visually appealing is typically left to the visual identity (VI) designer. Common types of CTA buttons include the following:
- Get a Quote Now: Set the button text as a call-to-action (CTA) with “Get a Quote Now” to enhance and encourage users to click and download the corresponding quotation plan or start a conversation via instant messaging tools to inquire about project pricing.
- Get a Solution Now: Set the button text as a call-to-action (CTA) with “Get a Solution Now”, similar to the above “Get a Quote Now”, to prompt and encourage users to click and obtain the solution or consult online. This can be used to download a corresponding solution PDF file or trigger an instant messaging tool to communicate with the website support team.
- Contact Us: The call-to-action (CTA) button “Contact Us” usually triggers one of two interactions upon clicking: one is to pop up an inquiry contact form window (it can also redirect to the Contact Us page), and the other is to directly open the instant messaging tool integrated into the website. The popup inquiry form method is generally more suitable for B2B websites, while triggering instant messaging for online consultation is more appropriate for B2C websites.
- Learn More: Similar to the above “Contact Us” CTA button, setting the button text to “Learn More” can serve as a prompt or encouragement for users interested in further understanding the products/services of the website. The stronger the user’s motivation to deeply understand the website’s offerings, the higher the conversion and deal rate.
- Submit Requirements: If the introduction of certain products or services on the website is clear enough, the call-to-action (CTA) button “Submit Requirements” can be used directly. This helps eliminate unnecessary intermediate steps. After clicking the “Submit Requirements” CTA button, users can directly discuss their needs with the website’s support or sales personnel, shortening the conversion path.
- Online Support: The call-to-action (CTA) button “Online Support” refers to the first red-box marked screenshot in this “Call-to-Action Button (CTA)” section, and involves the integration of instant messaging tools. As for which instant messaging tools to use on the website, it is recommended to make a decision based on the explanation in the “Online Contact” section. Various combinations of instant messaging tools can be used so that users can initiate communication conveniently by clicking the corresponding tool button to chat with the website’s support staff in real time.
- Call Now: If the website’s company has phone consultation staff, it is recommended to also design a call-to-action (CTA) button for the “Phone Number” on the site. Some users may prefer direct phone calls to communicate about products/services due to time-saving considerations. If the website’s offerings have high user value and strong advantages, providing a phone number as an inquiry method can help eliminate doubts and increase trust. When users on mobile or tablet devices (desktop cannot directly make calls) click the “Phone Number” CTA button, it will directly open the phone’s dial interface. The technical setup for the “Phone Number” CTA button is simple—just set the URL in the “Call Now” CTA button to tel:+PhoneNumber.
4. Quotation system
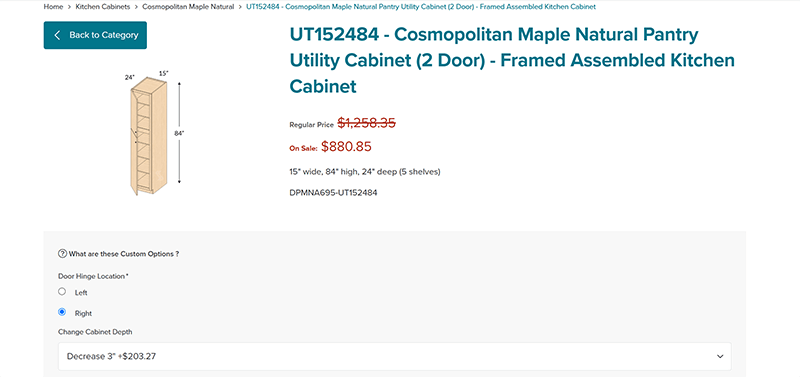
A quotation system on an independent website helps users efficiently and instantly obtain pricing plans for relevant products or services. At the same time, it allows the website owner to filter out inquiries from users whose needs do not match the offerings. When users obtain a suitable quote through a self-service process and still proceed with further consultation, they are often considered high-quality leads with a greater likelihood of conversion. This practical feature significantly reduces the workload of customer service roles and lowers the human resource demands for support staff within the independent site’s operation. The quotation system is particularly suitable for startup independent website businesses, which often lack sufficient manpower, resources, or funding. It helps relieve founders from spending excessive time on early-stage business communication by filtering out inquiries that do not carry real sales value. However, while the quotation system offers practical value, it also presents a budgetary challenge for startups. A fully functional e-commerce quotation system typically involves high development costs. According to Logic Digital Technology's experience, independent websites equipped with a quotation system are generally more established and tend to achieve better results in digital marketing efforts. Although a quotation system can improve marketing efficiency and enhance the user experience of obtaining pricing information, whether to include it should ultimately depend on the real needs and stage of development of the independent website business. The standard functions of a product quotation system are listed as follows:
- Model Selection: The quoting system provides independent website users with product model classification and filtering functions, allowing users to quickly find specific product models. The model list can be categorized and displayed by category, series, or function, and a search box using database-based Ajax request response technology is provided to facilitate precise queries by users.
- Specification and Size Selection: Supports users in selecting product specifications and dimensions according to their needs, such as length, width, height, color, or material. Options can be set as multiple or single selections to ensure flexible adaptation to different requirements.
- Configurable Dropdown Options: Provides users with optional configuration dropdown menus, such as additional components, upgrade features, or compatible devices. For computers or digital products, there are rich hardware configuration items. Dropdown menus make it easier for independent website users to make quick selections.
- Price Range Options: Allows users to set an acceptable product price range based on their budget to filter products. This helps users quickly find suitable products within their price expectations. A slider to adjust the price range or an input box to directly enter numerical values is also supported.
- International Shipping Carrier Selection: Provides multiple international shipping carriers for users to choose from. Users can select a courier service provider based on their daily usage habits, such as DHL, FedEx, and UPS.
- Shipping Cost Calculation: Dynamically calculates shipping costs based on country/region, product weight, volume, and shipping distance. Users can view detailed cost breakdowns in real time, ensuring accurate and transparent quotations.
- Order Quantity: Supports users in selecting or entering the required order quantity. Through frontend integration with the backend quoting system's algorithm, bulk discounts or minimum order quantity rules are automatically applied to meet the needs of users with different procurement scales. Generally, the larger the order quantity, the lower the unit price per piece (PCS), which offers price advantages for mass production.
- Estimated Delivery Time: Based on the product, quantity, and shipping method selected by the user, the quoting system triggers the delivery time algorithm to return the estimated delivery time (the time when the user receives the goods). The estimated delivery date range is displayed in the quoting system interface or data table.
- Instant Quote Button: Instantly generates real-time quotes based on the current selection. Price information is automatically updated using an asynchronous loading tech stack, allowing users to view the quote results immediately without refreshing the page, thus providing a convenient interactive experience.
- Export Quotation Data Table: The quoting system should also support exporting the quotation plan as PDF, Excel, or CSV format files. This allows users to save, print, or share the quotation information with their team.
5. Multi-language and multi-currency support
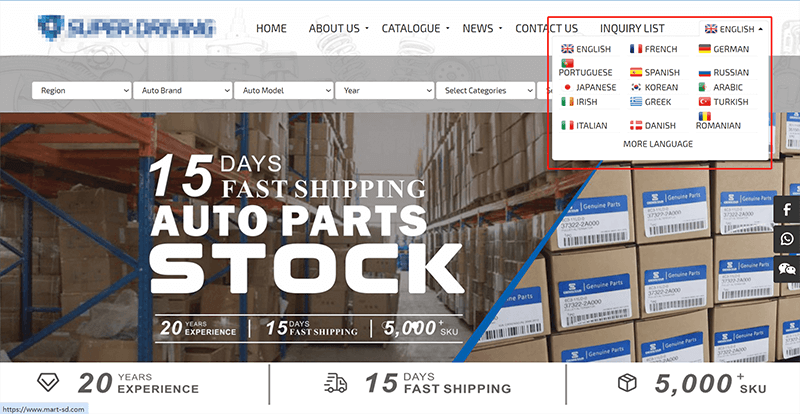
The necessity of multilingual support does not depend on whether the independent website follows a B2C or B2B business model. Whether an independent site requires multilingual support and how many specific languages are needed depends on the countries/regions where the business plans to operate. Languages for countries/regions not targeted for business do not need to be developed, and the number of languages selected will also impact the development costs of the site. When integrating multiple languages into an independent website, the language selector is integrated with the multilingual plugin. Once the machine or manual translation of page text is completed on the frontend/backend using the configuration features of the Multilingual Support Plugin, users can click on the corresponding language in the page's language selector, and the page will instantly switch to display content in that selected language. Whether the translation process is done via an online translation mode or via data retrieved from WordPress's MySQL database depends on the translation engine mode of the multilingual support plugin used. Multilingual support plugins that comply with SEO standards will store the page URLs and text keywords for each language version in the database. This way, search engine crawlers such as Googlebot or Bingbot can detect and index these different language versions into their search engine databases. Plugins that use a translation engine to perform static translations and store the translated page data into the independent website’s database include TranslateEasy developed by Logic Digital Technology, as well as WPML, and TranslatePress. On the other hand, another category of multilingual support plugins uses dynamic online translation technology such as GTranslate. This type of translation model, which dynamically converts page languages online, strictly speaking, does not comply with SEO standards. That’s because this method does not store translated page data in the independent website’s database. Similar to the Google Translate browser plugin, it uses a network-based online translation approach. Therefore, plugins using dynamic online translation modes can only satisfy users’ needs for reading page information in different languages, but they do not generate multilingual data that can be indexed by search engines.
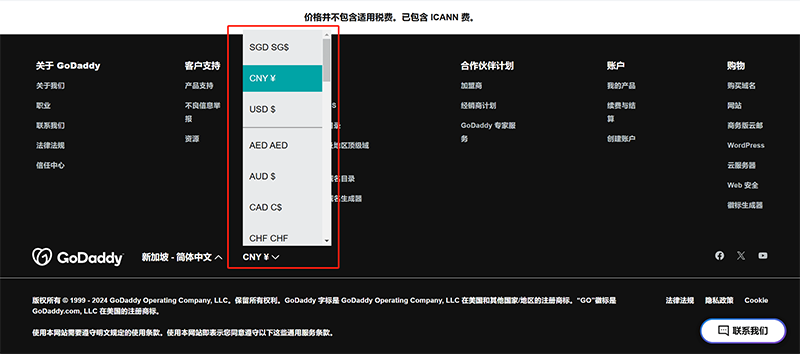
The need for multi-currency support on independent websites is the opposite of multilingual support. It is not a necessary function for both B2C and B2B websites. Multi-currency support is a typical feature required by B2C independent websites. Since B2B websites usually do not involve product sales or payment functionalities, this feature can be completely ignored for them. As shown in the screenshot above, the multi-currency support function in B2C independent websites allows users to select their local currency when browsing products and checking out. This enables them to view product prices and settle payments in their own currency, without needing to perform currency conversion calculations. Users can clearly understand product pricing at a glance. The multi-currency support function greatly enhances the convenience of payments for users, which plays a significant positive role in improving the conversion rate of consumer-facing independent websites. It reduces cart abandonment in the marketing funnel and boosts sales performance. It is worth noting that the multi-currency support function is provided through technical support from international credit card payment (acquiring) service providers, and is not developed by independent website development companies. Independent website development companies do not have the capability to develop international credit card acquiring systems themselves. Typically, these companies integrate with international credit card acquiring service providers, embedding their payment systems into the independent website to make the functionality operational.
2. Independent Station SEO Function
The SEO functionality of an independent website is actually not a highly complex engineering task for those with programming skills. Precisely because of this, the development budget for SEO functionality is suitable for both customized WordPress development websites and template-based website models. SEO functionality does not need to be distinguished by the type or business model of the website—it is an essential feature for any website. It’s hard to imagine anyone building a website today without the intention of driving traffic. SEO features, more specifically, involve converting various search engine-compliant HTML tags into visually operable fields through backend programming. These visual input fields appear in the page or article management interfaces, allowing independent site operators to input targeted SEO metadata for their pages. Below, I’ve listed the various required SEO features and provided descriptions for each one:
- sitemap configuration: A sitemap refers to the XML sitemap of the independent website. There are two types of sitemaps: one is an XML data source sitemap, and the other is an HTML sitemap. Based on practical experience with search engines, I personally believe that search engines primarily require XML sitemaps. As for whether HTML sitemaps are necessary, this remains a topic of some debate—some SEO practitioners believe that HTML sitemaps can also assist search engine indexing to a certain extent. Here, I will mainly explain the XML type of sitemap. An XML sitemap is a metadata file that must be provided to search engines. When submitting an independent website to a search engine, in addition to domain verification or DNS resolution of the domain, the sitemap must also be submitted. The content of an XML sitemap file is composed of dynamically generated URLs based on the independent site’s pages/posts. Without any custom programming, the sitemap file will automatically include the URLs of all published pages and posts. The key aspect of optimizing the sitemap is to control which pages/posts should be included in the sitemap and which page URLs should be excluded—specifically filtering out pages with no SEO value.
- robots.txt configuration: robots.txt, also known as the robots protocol, is a `.txt` text file that is either statically or dynamically generated by a website. The robots protocol is a standard followed by major search engines around the world for website data crawling. Similar to the sitemap, it is a site metadata file that must be submitted for search engine indexing. The robots.txt file can be configured using code to control whether the content of an independent website is allowed to be crawled by search engines (this assumes that the search engine adheres to the spirit of the robots protocol—some search engines or crawler programs may not follow the robots protocol and may crawl the site aggressively without respecting the settings in the robots.txt file). The robots.txt file is written using simple text directive language to allow or disallow search engine crawlers or bots from accessing the website. Similarly, it can also be used to allow or block access to specific directories of the site.
- Custom URL: The URL of an independent website can be customized using either pure static or pseudo-static permalink methods. Both pure static and pseudo-static have no impact on SEO. The standard for customizing a page URL on an independent website is to make its structure match the topic of the page. Although the URL of a page has relatively low weight in search engine algorithms and signals, a URL structure that is highly relevant to the topic of the page or article can help improve user experience by allowing users to understand the content of the current page just by looking at the URL suffix. However, it should be noted that the URL suffix is not recommended to be too long; it should be kept as short as possible. Long URLs are not friendly to either search engine bots or human readers.
- Custom Page Title: The page title here refers to the content of the page's
titletag, which is the title displayed in the browser's tab. Thetitleis the most important configuration item in terms of SEO weight. Thetitle, together with the customh1heading on the page, represents the theme of the page or article. It can be understood as the main idea of the page/article content, serving as the top level of the content structure, from which relevant subheading content is created top-down. - Custom Page Description: A custom page description refers to the content within the page’s
meta name="description" content, also known as the meta description. The meta description appears in the search engine's SERP. Although search engines will crawl the custom page description, they may not necessarily use it, as they often have a mechanism to automatically extract text segments that are considered most relevant to the user’s search query to display as the SERP description. A custom page description that is SEO-compliant and appealing can increase the click-through rate in SEO, thereby creating more conversion opportunities. On the contrary, if the page description is completely missing in the search engine's SERP, it may reduce the user's desire to click and view the page. This is because, based on the habits of most users, it is often difficult for them to fully understand a page's content by relying solely on the SERP page title. - Breadcrumb Optimization: Breadcrumbs refer to the position of the current page within the website structure, typically presented in a horizontal directory format beneath the page's navigation menu. Breadcrumb optimization offers two benefits for the page's SEO optimization. On one hand, breadcrumbs on the page help search engine crawlers better understand the structure of the website when indexing the independent site. On the other hand, for human reading experience, when users see well-optimized breadcrumbs on the current page, they can understand the page's position within the website structure and can navigate to the parent directory page by clicking on the breadcrumb links.
- Custom Nofollow: The HTML nofollow tag is an SEO tag that determines whether domain or page authority is passed. In SEO link building, the transmission of page authority for outbound links, inbound links (also known as external links), and internal links depends on the nofollow and dofollow tags. Specifically, the nofollow tag prevents the transmission of page authority from the current URL, while the dofollow tag allows the authority to be passed to the page linked.
- Custom Canonical: Canonical is an attribute value of the HTML code 'link rel' tag, used to set the canonical URL of the current page. The canonical URL refers to a situation where the same page generates multiple accessible URLs due to different categories or tags being applied. These different URLs all point to the same page. As a result, duplicate pages are created. Duplicate pages not only fail to be indexed by search engines but are also treated as duplicate content, which increases the difficulty of SEO management. To avoid the issue of search engines flagging duplicate pages, according to SEO standards, a canonical URL should be set for these different URLs that all point to the same page.
- Custom Meta Robots: Custom meta robots refers to the ‘meta name=”robots” content=”noindex or index” /’ HTML meta tag, which controls whether a page is allowed or disallowed from being indexed by search engines. In most open-source website building systems or SaaS website platforms, the default setting when publishing a new page or article is 'index', meaning the content of the page is allowed to be indexed. However, to improve SEO, a website will inevitably have some pages that have no indexing value for search engines. These pages with no indexing value should be set with 'noindex' as the attribute value.
- Custom Property: The property tag refers to the ‘meta property=”” /’ HTML tag. The purpose of the property tag is to optimize the social media sharing format, meaning it controls the display format when a page is shared on social media platforms. When an independent site's webpage is shared on social media platforms (such as Facebook, Twitter), the property tag’s attribute values can control the title, description, image, and other information displayed during sharing. For example, properties like og:title, og:description, og:image can be set to specify the title, description, and thumbnail image size when the page is shared.
- Custom Schema: Strictly speaking, there are two types of schema: one is the Schema.org structured data markup, and the other is the Google Schema structured data markup. The difference between the two is that schema.org is a common structured data standard shared by major search engines, while Google's Schema structured data markup is an extension of schema.org's structured data. Google's Schema structured data markup offers more diverse data structure types, which are customized by Google for their search engine. Both types of schema data markup can help search engines accurately understand the page data structure of an independent site, enhancing relevance and also helping pages appear in more enriched forms, such as rich snippets and knowledge graphs, in search engine SERPs, thereby improving click-through rates.
- Search Engine Resource Submission: After configuring the parameter values for the above SEO features, the primary task before launching and operating the independent site is to submit the website to search engines. Once the development requirements for the independent site are completed and the content on the pages is finalized, the site should be submitted to search engines for indexing, regardless of whether SEO work has started or not.
The twelve essential SEO features mentioned above are the technical aspects of SEO. Technical SEO forms the foundation of whether an independent site can perform well in search engine optimization, and it is a key indicator of an SEO expert's skills. Only by understanding the principles of technical SEO and properly deploying the necessary SEO code can one effectively test and verify search engine algorithms and signals. Technical SEO, content SEO, and link SEO follow a sequential order and should not be confused. Technical SEO is the underlying logic, and readers who aim to do SEO well cannot skip this essential lesson. This also indirectly reflects that once technical SEO is mastered, one can better grasp the algorithms behind search engine SERP rankings and the signals of content quality. From the perspective of SEO practice, I believe that a programmer’s comprehensive ability makes them the best candidate for an SEO expert, especially back-end developers. This is because most SEO tasks require logical thinking, and people with strong logical abilities can quickly observe and analyze the interconnected factors at the data level. An interesting phenomenon often arises when it comes to logical relationships: different people can grasp the logic of the same thing at different speeds. Some may understand it in a very short time, while others might never get it. The back-end developer role is one that heavily tests logical abilities, as coding requires logic every day, and coding logic is inseparable from algorithms. However, it is unfortunate that in reality, most programmers are either unwilling or not good at SEO work. This could be because the group itself has little interest in SEO, and the cause of this phenomenon may stem from the unique nature of SEO work. SEO spans three fields: one is the computer science aspect of internet principles, another is marketing and management knowledge, and the third is the literary and creative abilities (writing). The proportions of these three fields are not well-balanced, and, over time, the proportion of computer science in SEO is actually the smallest. Perhaps this is precisely why programmers with a computer science background often don't focus on SEO.
Ⅲ、Independent Website Product Display Features

Product display is an essential feature that independent websites must focus on designing well. The design of product display is the core part of the entire independent website design, around which key or auxiliary functional designs and visual page designs are created. If an independent website lacks product display, discussing conversion goals becomes meaningless. When planning the product display feature for an independent site, it is not enough to just understand the concept of "product display"; we must also master the methods of product display. Once we understand different product display approaches, we can effectively apply various product display features to the visual design of the website pages. A product display for a website selling goods is not a single form; it is generally a rich combination of multiple display methods. The product materials can be in image format, video files, or animation files. Below are the 5 types of product display methods organized by Logic Digital Technology:
1. Product window display (Banner display products)
The product showcase refers to the Banner position on an independent website page. Since the Banner occupies the prime position on the first screen of the page, it is also known as the window of the page. This is the first content area that visitors to the independent website will see when browsing the page. Therefore, the importance of the Banner is self-evident. It is the best place to convey brand impressions and display the products of the independent site. Given how crucial this page display area is, it would be a waste to use it solely for single product displays. It is recommended to set the Banner area to display the product categories of the entire independent site in different application scenarios. This can be presented in the form of images or videos showcasing various application scenarios. If image materials are chosen for the Banner area’s product display, the Banner area is typically developed as a carousel block to rotate through the image materials. The interaction method for the carousel can be set to autoplay or manual switching, allowing for a multidimensional and richer presentation of product elements. Video content or animations as Banner display materials have advantages over images in two main aspects. First, they enhance the liveliness of the page, improving the user experience on the independent site. Second, compared to static images, video or animation content can vividly showcase more product details.
2. Display of core products (main products)

Core products, also known as flagship products, are the main products or product series that an independent website emphasizes within its product lineup. While the display block for core products and the Banner display area are commonly placed on the homepage of the independent site, they are not exclusive to the homepage. Core product display blocks and Banner areas can be placed on any page of the site. The style of the core product display block is determined by the creative design of the visual identity (VI) designer. The design can vary infinitely, ranging from simple to complex. The purpose and commercial value of the core product display block is to increase the visibility of core or flagship products, thereby driving more inquiries or sales conversions.
3. Hot product display
Hot products and core products are not the same thing and should not be confused. The difference between core products and hot products lies in the fact that core products are those that the independent site owner subjectively decides to promote through the site's operations and marketing, whereas hot products are displayed based on the results of the programming logic algorithms developed for the independent site. The programming logic algorithm for displaying hot products can be based on product views to determine the ranking, or it can use the sales data of the independent site to control the product order within the hot product display block. Both product views and sales data are valid data sources that can be used for the hot product display algorithm. The purpose of placing a hot product block on the page is to guide users who are unsure about which product model to buy toward making a preferential purchase decision. These users do not have a clear purchasing target and will compare various product models across dimensions such as price, specifications, performance, and parameters, and then make a purchase decision based on the comparison results. Therefore, the products displayed in the hot product block can effectively meet the browsing and comparison needs of these users.
4. Product classification display

Product category displays can be presented on separate category pages, or—just like the screenshot above—can be designed and developed as product category display blocks to showcase product types. Compared to the navigation-style access to category pages, product category display blocks provide a more intuitive user interaction and experience, making it easier for users to navigate directly from the current page to the desired category. Placing product category display blocks on pages that match and are compatible with them allows users to gain a deeper understanding of the product series offered on the independent site, giving them more choices during product selection. This approach helps prevent users from abandoning their purchase when core products and hot products fail to meet their needs. It increases the possibility of conversion by satisfying a broader range of user demands, better retaining traffic, and reducing the loss of conversion opportunities on the site.
5. Product details page
The product detail page is the homepage for each product. The product detail page can be dynamically generated by the WooCommerce e-commerce system. Specifically, the operation is to list the product information in the WooCommerce e-commerce management system, which will then generate a corresponding product detail page. Alternatively, you can choose not to use the WooCommerce e-commerce management system to generate the product detail page in the usual way. Independent site businesses can choose the product detail page generation or development model based on their actual situation. For advice and guidelines on how to make this choice, you can refer to the article "Independent Site Development, Design, and Planning". A detailed explanation can be found in the section "Design of Marketing and Conversion Features for Independent Sites and the Role of Pages in Independent Sites." Compared to the four product display methods mentioned above, the product detail page, as the homepage for each product, has more detailed and rich content and page elements in terms of product display, because the four product display methods are based on regions (display blocks), while the product detail page is a full page. The product display elements in the product detail page are briefly explained in the list below:
- Product Name: The product name customized by the independent website enterprise. The product name can also include the product model.
- Product Price: The list price at which the product is sold.
- Product Add to Cart Button: A button that independent website users can click to add a product to their shopping cart list.
- Product order (checkout) button: A button that independent site users can click to directly purchase and check out.
- Product specifications: Product information such as size, color, weight, performance, etc.
- Product description: A text description that highlights the core selling points of the product and solves user pain points (user value).
- Product display pictures or product display videos: The product visual elements in the product display window can be divided into primary and secondary and sequential products with multiple angles to make them switchable or in a carousel format for users to browse. The material can be image files or video files to play and demonstrate the product.
- Product application scenarios or product instructions: Use a combination of pictures and text to show the product's usage scenarios or instructions. Convey the product's practical value to users, solve their potential needs, and help them establish an emotional connection.
- User reviews: Encourage users who have tried the product to leave reviews and display specific review content.
- FAQ: Answers to frequently asked questions about product usage, payment, shipping, after-sales support, product warranty, etc.
- Download: Download product-related documents.
Ⅳ、Independent Website Payment Features
The sales function of products on an independent site is essential for B2C independent sites, while B2B independent sites can ignore the payment functionality. The goal of a B2C independent site is product sales, and without a complete payment function as support, this goal cannot be achieved. Payment functionality is a general term; the underlying aspect is the various payment methods. Payment methods vary by region, but overall, the two main types are e-wallet payments and credit card payments. PayPal, as well as China's WeChat Pay and Alipay, are all e-wallet payment methods. In China, the usage habit leans towards using e-wallets rather than credit cards, while abroad, the use of both e-wallet payments and credit cards is more balanced, with both types being widely used. In the US and Europe, data shows that about 37% of US consumers prefer using PayPal for online shopping, and about 82.8% of the top 1000 retailers in North America and Europe accept PayPal payments. According to data from EcommerceDB, the UK is the country in Europe with the highest use of PayPal, with approximately 330,000 daily active users, accounting for about 0.5% of the UK's total population.
After explaining the payment methods for product sales on an independent site, it is also necessary to explain the technical implementation of the payment function to readers. This will help businesses planning to build a B2C independent site understand the technical relationships involved and avoid confusion between the independent site development company and the third-party payment gateway providers. The independent site development company itself does not have the capability to develop international credit card payment/settlement systems. The entire payment system is provided by third-party international credit card payment gateway providers, such as 2checkout, Oceanpayment, Airwallex, etc. Therefore, B2C independent site businesses need to assess and choose their own third-party international credit card payment gateway providers. The independent site development company, as the technical development party, is responsible for integrating the third-party international credit card payment system into the independent site to enable the checkout function when users proceed to checkout. The principle of PayPal is similar; once the independent site business has completed the application for a PayPal business account and obtained the usage rights, our development company will integrate PayPal into the independent site to enable normal payment processing.
- PayPal: PayPal is the world's most widely used electronic payment system, and its usage volume dictates that all B2C independent sites must integrate PayPal as one of the payment options available for users. Readers who are unsure about how to apply for a PayPal business account can refer to the article "How to Register a PayPal Business Account" and follow the steps outlined in the article to apply for a PayPal business account. Please note, it is essential to apply for a business account, not a personal account.
- International Credit Card Payment Gateway System: The payment system supports independent site users to checkout using international credit cards such as JCB, VISA, American Express, MasterCard, and Diners Club. Readers interested in learning more about integrating international credit card organizations' payment systems into independent sites and how to set it up can refer to the article "How to Set Up Payment on Independent Sites? Tutorial on Integrating Payment Features".
Ⅴ、Independent Website Security and Privacy Features
The security and privacy features of an independent site involve the data security of the independent site business and the security of user information. These are essential functions for the safe operation of the independent site. Without security and privacy features, there is a risk of leakage of business data and user information, as hackers can exploit vulnerabilities in the absence of security and privacy features to invade the site and access the site's and users' information. Once this information is leaked, it not only causes users to lose trust in the independent site but may also lead to legal disputes and financial losses. Therefore, independent sites should adopt a multi-layered defense strategy, including enabling SSL encryption protocols, privacy policies and GDPR compliance, and firewalls for attack protection, to ensure the comprehensive protection of information security and privacy. At the same time, independent site businesses should clearly define their privacy policies and transparently inform users about data collection, usage, and storage methods, ensuring that users are informed and protected. These measures are not only a reflection of the independent site's responsibility but also an important means to gain user trust in the competitive market. Additionally, in terms of user experience, if the independent site fails to implement SSL encryption and HTTPS encryption functions, it will be blocked from access by browsers that have high user privacy protection requirements, such as Microsoft's Edge and Google's Chrome browsers. When users input a domain name or URL without SSL encryption and HTTPS, the page will not be accessed directly. The browser will interrupt access and display a warning message that the URL is unsafe. The lack of SSL encryption and HTTPS creates a terrible user experience, which can be fatal to the independent site.
1. SSL encryption and HTTPS
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) is a security protocol used to establish a secure connection between a client (such as a browser) and a server. Through SSL encryption, independent websites can:
- Protect data privacy: All transmitted data will be encrypted to prevent it from being stolen or tampered with by middlemen (such as hackers).
- Verify identity: Verify the true identity of the website through the SSL certificate to prevent users from visiting fake websites.
- Prevent data tampering: Data is integrity protected during transmission to ensure it has not been modified.
HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) is a hypertext transfer protocol based on SSL/TLS encryption. It adds a security layer to the HTTP protocol to make website communications more secure. Website addresses using HTTPS start with "https://" instead of "http://". Specific functions include:
- Encrypted communication: All data will be encrypted before transmission to prevent sensitive information (such as passwords, credit card information) from being leaked.
- Identity authentication: Use digital certificates to ensure that users are visiting legitimate websites, not fake or phishing websites.
- Data integrity: prevents data from being hijacked or tampered with during transmission.
2. Privacy Policy and GDPR Compliance
The Privacy Policy and GDPR Compliance feature is a mandatory requirement imposed by the European Union to protect users' privacy rights and personal data security, ensuring that businesses handle user data with legal legitimacy and transparency. These requirements stem from the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), a comprehensive privacy regulation established by the EU that is binding on all websites dealing with EU user data. If an independent site has not developed or enabled the privacy policy and GDPR compliance features, even if the site's pages are targeted in Ads campaigns for European countries, they will not be able to effectively display and gain traffic in the search engine SERP of those countries. It is still unknown whether SEO will be affected, as my company primarily operates in Chinese-speaking regions and we have not tested data in English-speaking regions yet. Privacy protection policies for individuals on the internet are a trend for the future of the internet, and it is recommended that independent sites make privacy policy and GDPR compliance features a mandatory part of their site design and planning.
3. Firewall and anti-attack protection
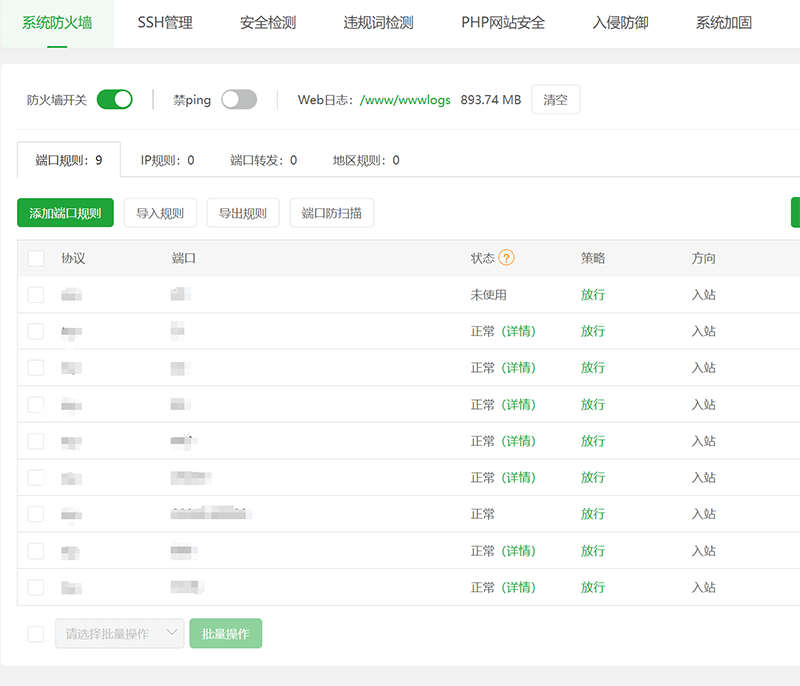
Firewall and attack protection are essential measures for independent sites to prevent network attacks. The firewall and attack protection functions are core components of modern network security systems, designed to prevent malicious attacks, unauthorized access, and data breaches, ensuring the secure operation of the independent site, server systems, and web programs. The main functions of a firewall include traffic filtering, which can filter traffic based on rules such as IP addresses, port numbers, and protocol types, blocking suspicious or unauthorized access. It also has the capability to detect abnormal behaviors (such as port scanning or brute force attacks) and intercept potential intrusion attempts.
VI、Independent Site Data Analysis and Conversion Tracking Function

Data analysis and conversion tracking are key tools for successfully conducting internet marketing on independent sites. Through data analysis, operators can fully understand visitors' behavior, including the sources of visits, duration of stay, browsing paths, and conversion points. These data not only serve as the foundation for optimizing user experience but also play an important role in developing marketing strategies. Without data analysis, operators cannot clearly know which promotional channels are most effective, nor can they accurately determine which content best attracts the target audience’s interest. Conversion tracking is the core tool for turning traffic into revenue. It helps operators understand where potential issues may exist, such as why users are dropping off on the shopping cart page, which product pages have low conversion rates, and whether promotional campaigns have achieved the desired results. By tracking and analyzing this information, operators can make targeted adjustments to page design, optimize product pricing, or refine promotional strategies to improve overall conversion rates. Without data analysis and conversion tracking, internet marketing would undoubtedly fall into a blind state, much like a blind person walking without knowing the direction. Independent site operators would not only waste a significant amount of promotional funds but could also lose market share due to ineffective decisions. Therefore, operators must prioritize the development and optimization of these functions to ensure that traffic efficiently converts into actual revenue, enabling them to secure a place in the highly competitive market.
1. Traffic and User Behavior Analysis
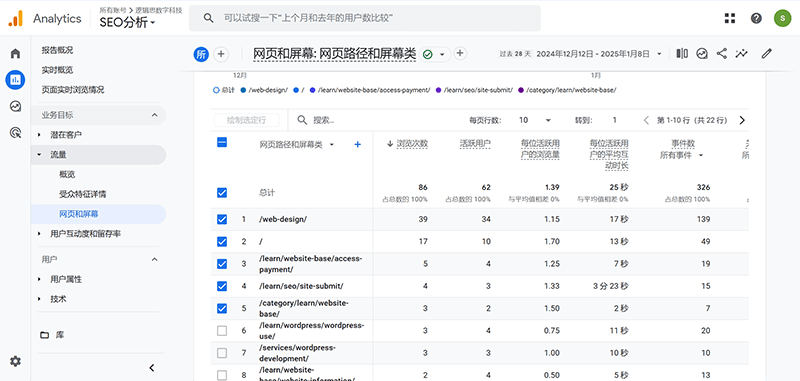
The best tool for analyzing traffic and user behavior on an independent site is Google Analytics. Google Analytics provides very rich and comprehensive dimensions for traffic data and user behavior analysis on independent sites. Through the analysis of these metrics, independent sites can more accurately understand traffic sources, user behavior, and key conversion paths. In terms of traffic analysis, Google Analytics offers multiple dimensions, including traffic sources, channel types, and geographic locations. The traffic source dimension helps independent site operators understand whether users are entering the site through search engines, direct visits, social media, or paid ads. This not only helps evaluate the effectiveness of different marketing channels but also optimizes advertising budget allocation. The geographic location dimension reveals the regional distribution of visitors, which is particularly important for independent sites with localized promotional strategies or international operations.
User behavior analysis is another core function of Google Analytics. Through behavior metrics, independent site operators can dive deep into users' stay duration, bounce rates, page views, and visitors' paths on the site. Stay duration and bounce rates reflect how attractive the content is to users, while page views serve as an important basis for evaluating the value of a page. Path analysis helps operators understand the interaction patterns of users on the site, such as how users enter a specific product page from the homepage and eventually complete a purchase. This data provides valuable insights for optimizing the site’s structure and content.
2. Inquiry Conversion Tracking
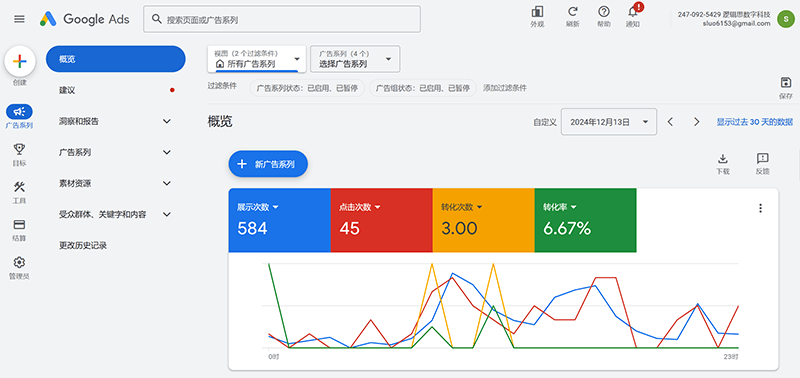
Inquiry conversion tracking for independent sites is a key link in evaluating and improving the effectiveness of internet marketing. Metrics such as user sources and inquiry conversion rates provide important data to optimize marketing strategies. Through detailed analysis of these data, businesses can gain a comprehensive understanding of user behavior patterns, identify issues in marketing efforts, and continuously optimize and enhance the conversion capabilities of their independent sites. The source of users is the starting point for inquiry conversion analysis. By tracking whether users come to the independent site through search engines, social media, emails, paid ads, or direct visits, independent site businesses can clearly identify which channels bring in more high-quality traffic. For example, if it is found that traffic from a certain social media platform is high but the conversion rate is low, it may be necessary to adjust content marketing strategies or promotional methods to enhance the relevance and appeal of the content. On the other hand, if traffic from a certain search engine ad results in a high inquiry rate, the budget for that ad can be increased to further expand customer acquisition. Inquiry conversion rate is the key metric that measures the process of a user converting from a visit to actually submitting an inquiry. With conversion rate data, independent site businesses can accurately assess the page’s conversion capability. If the conversion rate for certain product pages is low, it may be due to unclear page design, uninspiring content, or a complicated form-filling process. By optimizing page layout, enhancing visual appeal, providing stronger product information, or simplifying inquiry forms, the inquiry completion rate can be effectively increased. Additionally, monitoring conversion rates among different user groups, such as new visitors vs. returning visitors, can help independent site businesses develop more targeted marketing plans.
VII. Independent Site Social Media Integration Functions

The integration of social media features can bring multiple positive effects to an independent site. It not only enhances user interaction and brand exposure but also improves traffic conversion efficiency. By integrating social media features into the independent site, the traffic sources of the site can be significantly boosted. Through features such as embedding social sharing buttons and dynamic content synchronization, users of the independent site can easily share content from the page to their social media accounts. This not only expands the reach of the content but also attracts more potential users to visit the independent site. For example, when visitors are browsing blog posts or product pages, they can share the content to their social media feeds with one click, allowing more people within their circles to see and become interested, thereby creating a word-of-mouth effect that reaches more people who might need the product or service. Furthermore, the integration of social login functionality optimizes the user experience and lowers the registration barrier. When an independent site allows users to quickly log in or register using their social media accounts, it not only simplifies the cumbersome account creation process but also increases user convenience. This approach effectively reduces user churn and helps the independent site accumulate real user data, enabling operators to better understand and analyze user interests and behavior patterns, thus achieving more precise content delivery.
Conclusion: The article "Essential Functional Requirements for Building an Independent Site" focuses on the key features required for a well-functioning independent site, but it may not cover all aspects of the independent site comprehensively. Therefore, if readers feel that this article only addresses the essential features of an independent site and are interested in the overall design, development planning, and operational strategy of an independent site, they can click on the previously published article by Logic Digital Technology, "Independent Site Design, Development Planning, and Operations." This article provides a more systematic explanation of the role of independent site pages, creative design methods for independent sites, and internet marketing channels for independent site operations. The article also offers suggestions for internet marketing strategies in independent site operations.
Finally, for readers who have made it this far, if your time is limited and the cost of investing in technical learning and practice is high, and you have no intention of deeply engaging in technical work, this article may only serve to help you understand the features that an independent site needs based on its business model. If you do not plan to handle the technical work yourself and prefer to entrust it to a more experienced team, we recommend choosing professional services. The Logic Digital Technology team specializes in WordPress website building and technical development. If you wish to delegate the development and implementation of an independent site, feel free to contact the Logic Digital Technology team, and we will provide you with efficient, professional solutions.
Logic Digital Technology (SZLOGIC) All rights reserved. This article is welcome to be shared by individuals to help newcomers entering the cross-border e-commerce independent website track, but reproduction for commercial purposes is prohibited.