Domain Registration and Domain DNS Resolution Tutorial

Before creating a website, the first step is to register a domain name that matches your company/brand/product. Many novice readers planning to create a website for the first time are unfamiliar with the process of registering a domain name and setting up DNS resolution. In this article, we will use well-known domain registrars both domestic and international as examples, providing a step-by-step guide with images to teach you how to register your desired domain and handle DNS resolution when using the domain. Even if you don't intend to Build a Website, after learning this tutorial, you will be able to effectively manage your domain registrar’s backend and handle DNS resolution on your own. Registering a domain name and managing DNS resolution only requires a basic understanding of domain-related knowledge, without delving into deep technical expertise, so you can easily do it yourself.
By reading the "Domain Registration and Domain DNS Resolution Tutorial," readers will be able to find a suitable domain registrar for their website without requiring any computer science knowledge. They will understand that different regions require different domain registrars for domain registration, and learn how to configure DNS resolution for their domain. The article will also teach:
- The importance of domain extensions for website use
- Policy requirements of domestic and international domain registrars
- Functions of domain management
- DNS parameters and the correct parameter values
The "Domain Registration and Domain DNS Resolution Tutorial" will be divided into the following four sections. If readers have already registered a domain but have not configured DNS resolution, they can directly click on the "Domain DNS Resolution" section link to read that part quickly.
- Choosing a Domain Registrar
- Find domain names, domain extensions and choose domain names
- Domain Management
- Domain name DNS resolution
Ⅰ、Choosing a Domain Registrar

Choosing a domain registrar should match the country/region where your website operates. In general, there are two categories: if your website operates within China, you should choose a domestic domain registrar, and if your website operates internationally, you should choose an international domain registrar. The reason for this is twofold. First, domestic domain registrations require filing with the relevant authorities, while international domains do not have such filing requirements. Secondly, there is a difference in the available ccTLD (country code top-level domain) and gTLD (generic top-level domain) choices. For instance, domestic registrars do not offer options like .us or .org, but international registrars do. Thirdly, different domain service providers have different locations for their domain servers. If a foreign domain server resolves to a domestic website hosting server, or vice versa, this can cause delays. These factors can hinder website operations. Therefore, selecting a registrar based on your website's operational region can reduce unnecessary workload, improve website loading speed, and offer more choices in domain selection.
1. Domestic domain name registrar

- Aliyun: Aliyun is a well-established domain registrar. Aliyun's domain registration system originated from Wanwang, which was founded in 1996 and was one of the early domain registrars in China. In 2013, Alibaba acquired Wanwang and integrated its domain registration system into the Aliyun ecosystem. Due to the advantages of integrating with Aliyun's ecosystem, Aliyun's domain registration market share still ranks first in China. In addition to a large selection of domains with the .cn suffix, Aliyun's domain registration system also offers the widest choice of gTLDs that are allowed for filing under domestic policies.
- Xinnet: Xinnet, formally known as Beijing Xinnet Digital Information Technology Co., Ltd., was established in 1993. Like Aliyun's domain registration system, which originated from Wanwang, Xinnet is also a long-established domain registrar in China and holds a significant market share in the domestic domain registration market. Similarly, Xinnet's competitiveness in the stock and selection of .cn domains and gTLDs is not inferior to that of Aliyun. Due to the slowdown in the growth of the domestic PC internet, Xinnet's business development in recent years has increasingly shifted towards an ecosystem development approach.
2. Foreign domain name registrars

- GoDaddy: GoDaddy is a well-known internet company headquartered in the United States, established in 1997. It is the largest domain registrar in the world. GoDaddy offers a wide range of domain registration services, allowing customers to register various top-level domains (TLDs), including .com, .net, .org, etc., as well as various country code top-level domains (ccTLDs), such as .cn, .uk, .jp, etc. In addition, GoDaddy also provides domain trading, domain hosting, domain protection, and domain management services.
- Namecheap: Namecheap is a well-known domain registrar and internet service provider headquartered in Los Angeles, California, USA, established in 2000. Namecheap offers a wide range of domain registration services, allowing users to register various top-level domains (TLDs) and country code top-level domains (ccTLDs), such as .cn, .uk, .jp, etc.
Ⅱ、Find domain names, domain extensions and choose domain names
After readers have reviewed the domestic and international domain registrars listed above and made a choice, they can proceed to register a user account on the domain registrar's website. Once the account is registered, they can log in (login is required to place an order and register the domain) and proceed with searching for a domain, selecting a domain name, and choosing the domain extension. However, domain registration is often not 100% as planned because domains are unique virtual assets. Even though there are different domain extensions, their numbers are always limited, and many strange extensions are not acceptable. Furthermore, domains have been in use for decades, and many easy-to-read, easy-to-remember, or word-based domains have already been registered, making it difficult to find available ones today. Here, I would like to share a small trick for domain registration. Although it is a fallback solution when the ideal domain is unavailable, it still serves as a good backup option. This trick is to divide the domain registration plan into a primary and a secondary plan. For example, the primary domain registration plan for Logic Digital Technology was initially "logic," but both the .com, .net, and .org extensions had already been registered. Therefore, the secondary plan was used, which led to the current "szlogic.net." By adding "sz" (the abbreviation for Shenzhen, where the company is located) in front of "logic," the domain was successfully registered. In summary, the small trick for domain registration is to add some creativity to the original domain name when the primary option is unavailable. This often allows for successful registration, and readers can use this technique for their own domain registration.
1. International top-level domain name suffix

If you're unsure about how to choose a domain extension, let me briefly explain. Generally, the first choice is to select an international top-level domain (gTLD). However, with the development of the internet, there are now many gTLDs—several dozen, and some extensions that are rarely seen in our daily browsing, such as .coop, .name, .biz, etc. These newer domain extensions have low recognition among internet users and therefore have limited investment value. We should focus on the three oldest and most suitable international top-level domain extensions for personal and commercial use: com, net, and org. When selecting, we can follow the order of com-net-org. First, choose the most commonly used commercial domain, com. If com is already taken, choose net. If net is also unavailable, opt for org. However, it's important to note that org cannot be applied for or registered in Mainland China. If your website is not operated in Mainland China, an org domain is not inferior to a net domain. In fact, for a long period, org domains were not allowed for personal or commercial use and were exclusively reserved for non-profit organizations and government entities. The com, net, and org domains were the first batch of domains created when the internet launched in January 1985. As for country code top-level domains (ccTLD), if the website is targeting a specific country or region, the best choice for a domain extension is not necessarily com, net, or org, but the country code domain extension, because it allows both users and search engines to immediately identify the website's country, region, and language attributes.
2. Domestic domain name registrars search for domain names and select domain name suffixes
Taking Alibaba Cloud, a domestic domain name registrar, as an example, log in to Alibaba Cloud's domain name registration page. After logging in to your user account, the Alibaba Cloud domain name search interface is shown in the red box in the figure below. Enter the domain name you want to register in the domain name search input box, and select the country suffix or international common suffix that matches your website in the domain name suffix selection box. After entering, click the "Query Domain Name" button.

The domain query result page on Alibaba Cloud is shown in the image below. In this example, I entered "inlibala" as the domain query term, and used the default top-level domain suffix ".com." The query results show that both the top-level ".com" and the country-specific top-level ".cn" are available for registration. This is a very good outcome. If readers also get such satisfactory results when querying their desired domain, they can simply click the "Add to List" button on the right side to proceed to the next step and complete the payment for domain registration.

3. Search for domain names and select domain name suffixes at foreign domain name registrars
For foreign domain registrars, let's take Godaddy as an example. As a domain registrar not subject to the domain registration policy restrictions, Godaddy offers more domain suffix options. After registering and logging into Godaddy, the domain search interface is shown in the image below. In the input box marked by the red box in the image, you can enter your desired domain name keywords. Godaddy's search box does not have a specific option for choosing domain suffixes; you simply enter the complete domain name along with the suffix you want, and it will perform a search that includes the suffix. The suffix you entered will be prioritized in the search results. After entering, click the "Search Domains" button on the right to begin the query. There are two things to note when using Godaddy for domain registration. First, to properly access the Godaddy website, you need to enable a VPN. Second, if the Godaddy page is not in Chinese, you need to select Chinese from the language options in the footer of the website, or else you won't be able to use Alipay to pay for the registration fee.
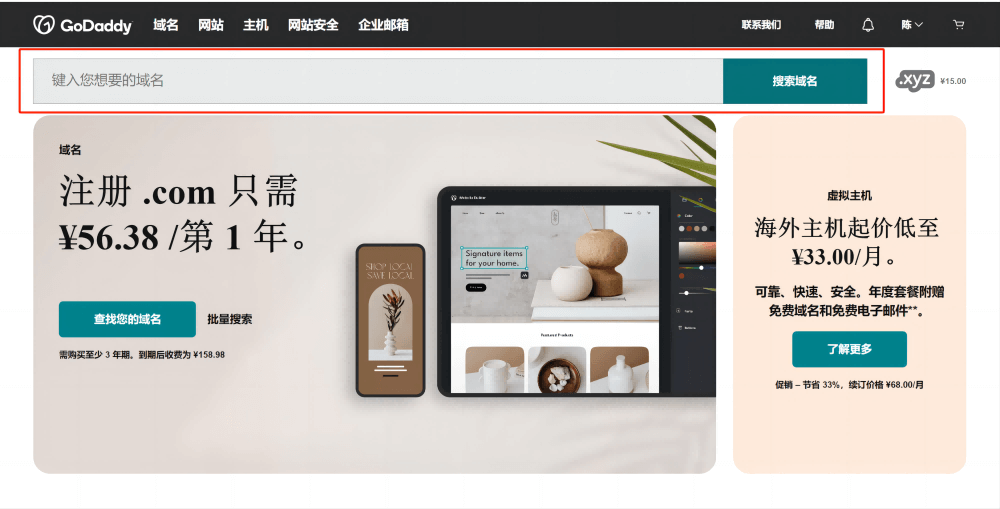
Using "inlibila" as the search keyword for the domain, the domain search results from Godaddy are shown below. The results indicate that the domain "inlibala" offers more suffix options available for registration than Alibaba Cloud. In addition to the same ".com" and ".cn" suffixes available on Alibaba Cloud, there are more suffix options to choose from. If you enter the actual domain you want to register, it will also provide satisfactory results, such as "inlabila". You can directly select the domain suffix you prefer, click the "Add to Cart" button on the right, and proceed to the next step to complete the payment for domain registration.

Ⅲ、 Domain Management
After successfully registering the domain, you can find the domain management section under "My Products" in the domain registrar's user account. This section will list the domains associated with the user's account, and you can manage these domains using standard domain management functions. These management functions are internationally recognized and are commonly available across different domain registrars without significant differences. The available management functions include: DNS records, forwarding (redirection), domain transfer, and domain nameservers. Below are the domain management operation pages for Alibaba Cloud and Godaddy, along with a list of the definitions of the four commonly used domain management functions: DNS records, forwarding (redirection), domain transfer, and domain nameservers.
Alibaba Cloud domain name management operation function diagram

Godaddy domain name management operation function diagram

- DNS Records: DNS (Domain Name System) refers to the system that manages domain names. Under the DNS records function, you can add or delete DNS resolution records. A domain name cannot be used on its own; it needs DNS resolution before it can be used (the domain name can only be accessed after DNS resolution). If the term "DNS resolution" feels unfamiliar, you can think of "DNS resolution" as "DNS mapping." This means that to use a domain name, you must first map it to the specified server's IP address in order to access the server using the domain name. Therefore, DNS resolution can also be viewed as the mapping relationship between a domain name and an IP address.
- Forwarding: Forwarding refers to redirecting, which means setting up forwarding rules within the domain forwarding function. These rules include: the type of redirection (the redirection status code, 301 or 302), the target domain name for the redirection, etc., which allows the redirection between domains. For example, currently, both szlogic.net and szlogic.org are domains under Logic Digital Technology, but the active domain is szlogic.net, while szlogic.org is unused. To prevent a 404 error when accessing szlogic.org, I have set up a forwarding from szlogic.org to szlogic.net. Therefore, when visiting szlogic.org in the browser, it will redirect to szlogic.net.
- Domain Transfer: The domain transfer function has two types. One is to transfer the domain to another account, meaning the domain can be transferred. The other is to transfer to a different registrar. For example, a domain purchased from Aliyun can be transferred to GoDaddy. Once successfully transferred to the new registrar, the domain can be managed within the user account of the new registrar.
- Domain Name Servers: The default domain name server address is the address of the domain registrar. If no domain hosting operation is needed, you can keep the default. However, if you need to host the domain, you will need to change the domain name server address to the address of the domain server of the hosting provider. For example, when performing CDN operations, you would generally need to change the domain server address to the domain server address of the CDN service provider.
Ⅳ、Domain name DNS resolution

The DNS resolution function of a domain refers to the process of converting the domain name into the corresponding IP address. When you type a domain name into your browser, such as "szlogic.net," your computer needs to know the IP address of the web hosting server that corresponds to "szlogic.net." This server's IP address is set in the domain management's DNS records function, which maps the domain's DNS to the server. This allows the computer to establish a connection with the server and retrieve the web page content. This is when the DNS resolution process comes into play.
1. The principle of DNS resolution
- When you enter a domain name, such as "szlogic.net" in your browser, your computer will first send a query request to the local DNS server.
- The local DNS server will first check its cache to see if it already has the IP address for the domain name. If so, it will return the IP address of the website server directly to your computer.
- If the local DNS server's cache does not contain the corresponding IP address for the domain, it will send a query request to the root name server.
- The root domain name server tells the local DNS server which top-level domain name server it should send a query request to, such as the ".net" top-level domain name server.
- The local DNS server then sends a query request to the top-level domain name server, asking for the address of the authoritative domain name server for the domain name.
- The top-level domain name server will reply to tell the local DNS server which authoritative domain name server should send the query request to. This authoritative domain name server is usually managed by the registrar of the domain name.
- The local DNS server eventually sends a query request to the authoritative domain name server and obtains the IP address of the website hosting server corresponding to the domain name.
- The local DNS server returns the obtained IP address to your computer and caches the query result to speed up the query next time the same domain name is queried.
- Your computer uses the obtained IP address to establish a connection with the server and start fetching web page content.
2. Demonstration of DNS resolution operation steps
The names of the function entry points and operation buttons may vary slightly between different domain registrars, but they are essentially the same. For example, the DNS resolution function entry in Alibaba Cloud is called "Resolution Settings," while in GoDaddy, it is called "DNS Records." Once you understand this, you don’t need to worry too much during actual operation—it’s just a different name for the same thing. You can proceed with the operation as usual.
Step 1. Click the "Add Record" button of DNS resolution, as shown below:
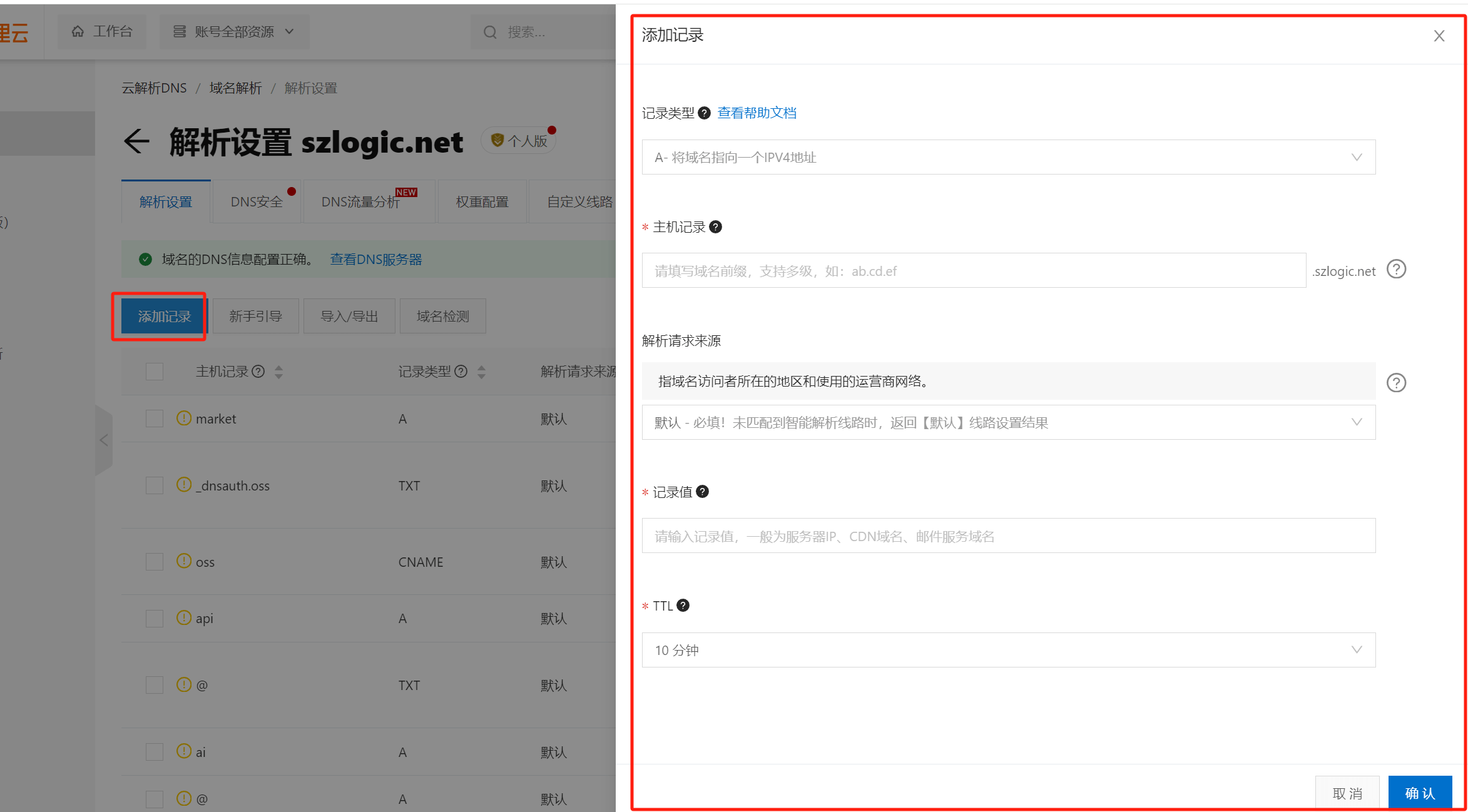
Step 2: Enter the parameter values of DNS resolution in the setting window on the right. Before entering the parameter values, we need to know the definition of each parameter. The definition of each parameter is as follows:
- Record Types: There are many types of DNS records. To avoid involving too much technical content in this article, we will only explain the A record. The A record is used to map a domain to the IP address of the web hosting server. "A" stands for Address record, and the A record is used to specify the IP address of the server corresponding to the domain. It can also be used to enable subdomains of the domain.
- Host Record: The host record here refers to the domain address being resolved. Many beginner readers may wonder at this point, isn't the domain just the domain we registered? What is this domain address? Actually, it is not quite so. The domain we register is actually the main domain, and theoretically, unlimited subdomains can be created under the main domain. Let’s use an easy-to-understand example: for Tencent's qq.com, qq.com is the main domain, while news.qq.com and mail.qq.com are subdomains of qq.com, representing the news and QQ Mail services, respectively. Therefore, the parameter value for the host record should accurately specify which domain should be mapped to the hosting server of the website. If you are resolving the main domain, you need to create two DNS records, one with the host record as @, and the other with the host record as www. These two newly added DNS resolution records have the same record type, resolution request source, record value, and TTL, except for the host record.
- Resolution Request Source: The "Resolution Request Source" feature is available in Alibaba Cloud's domain settings, but GoDaddy does not have this feature. This feature allows you to specify the feedback results when users in different regions or using different network operators access the domain. For this feature, it is recommended to keep Alibaba Cloud's default route.
- Record value: The IP address of the website hosting server. Just enter the IP address into the input box of the record value.
- TTL: The TTL (Time to Live) value refers to the duration that a domain resolution record is stored in the DNS server. When DNS servers located in various regions receive a resolution request, they will send a resolution request to the domain's designated DNS server to obtain the resolution record. Once this record is obtained, it will be stored in the DNS server for a period of time. During this time, if another resolution request for the same domain is received, the DNS server will not send a request to the DNS server again but will directly return the previously obtained record. The duration for which this record is stored in the DNS server is the TTL value. Therefore, TTL is not an input field but a selectable option in a dropdown menu, and its value is in time units. It is recommended to set the TTL parameter value to the shortest time of 10 minutes.
Step 3. After filling in the information correctly, as shown in the figure below, click the "Confirm" button to complete the setting of domain name DNS resolution.
The correct format and parameter values for the main domain's DNS resolution are shown in the image below (the two A records created). After configuring the DNS resolution, click confirm. It will generally take around 10 minutes to take effect. You can directly visit the domain to check if it's working, or you can click the "Check Effect" button on the right side of the resolution record to test whether the domain resolution has taken effect.
The host record value is: @

The host record value is: www

Conclusion: The above is the complete guide for domain registration and adding domain DNS resolution. Choose a domain registrar based on the region where your website operates, and use the domain registration tips and steps shared in this article to register your domain. When the primary domain option is no longer available, you can get creative with the domain name, and this approach generally provides good alternatives. In actual domain application, understanding the DNS resolution parameters explained in this article and filling in the DNS parameter values correctly will ensure proper configuration.
Finally, if you are planning the development of a website and wish to secure a suitable domain by registering it under your name before officially starting the project development and domain resolution, and you need professional advice and a website development plan during this process, feel free to contact the Logic Digital Technology team. The Logic Digital Technology team specializes in WordPress website development and technical development. We will provide you with efficient and professional solutions to ensure the smooth implementation of your website development project.
Logic Digital Technology (SZLOGIC) All rights reserved. Reproduction is prohibited.